Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and chronic respiratory conditions, have become leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Lifestyle factors play a critical role in both the prevention and management of these conditions. Understanding how everyday choices impact chronic disease can empower individuals to make healthier decisions and improve their quality of life.
The Connection Between Lifestyle and Chronic Disease
Lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption significantly influence the risk of developing chronic diseases. For instance:
- Diet: A diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats is linked to conditions like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports heart health, regulates blood sugar levels, and reduces inflammation.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, improves cardiovascular health, and enhances insulin sensitivity. Physical inactivity, on the other hand, contributes to weight gain and increases the risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease and diabetes.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a major risk factor for chronic diseases including lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and heart disease. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of these conditions and improve overall health.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is associated with liver disease, certain cancers, and cardiovascular issues. Moderation and responsible drinking habits are essential for reducing these risks.


Strategies for Prevention and Management
1. Adopting a Balanced Diet
Incorporate a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your diet. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a colorful array of fruits and vegetables. Reducing salt, sugar, and processed foods can lower the risk of hypertension, diabetes, and other chronic conditions.
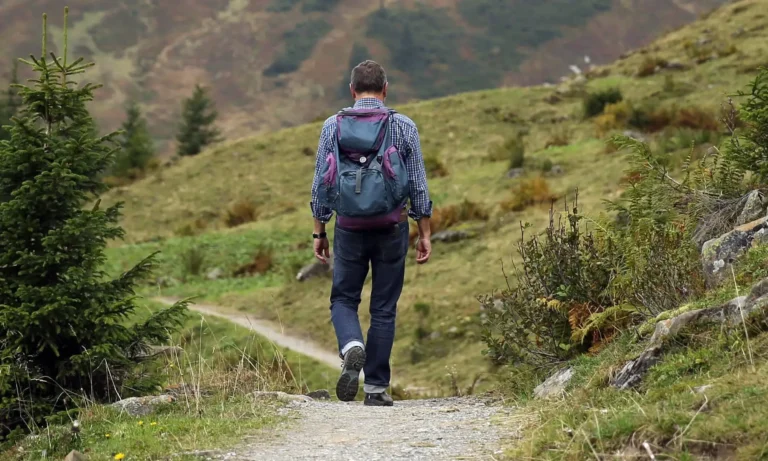
2. Engaging in Regular Exercise
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week, combined with muscle-strengthening exercises on two or more days. Regular physical activity supports weight management, improves cardiovascular health, and enhances overall well-being.
3. Avoiding Tobacco and Limiting Alcohol
If you smoke, seek support to quit, and avoid environments where smoking is prevalent. Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels—up to one drink per day for women and two for men—to reduce the risk of chronic disease.



4. Managing Stress and Mental Health
Chronic stress can contribute to various health issues, including heart disease and hypertension. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises. Additionally, maintaining strong social connections and seeking professional help for mental health issues can support overall well-being.
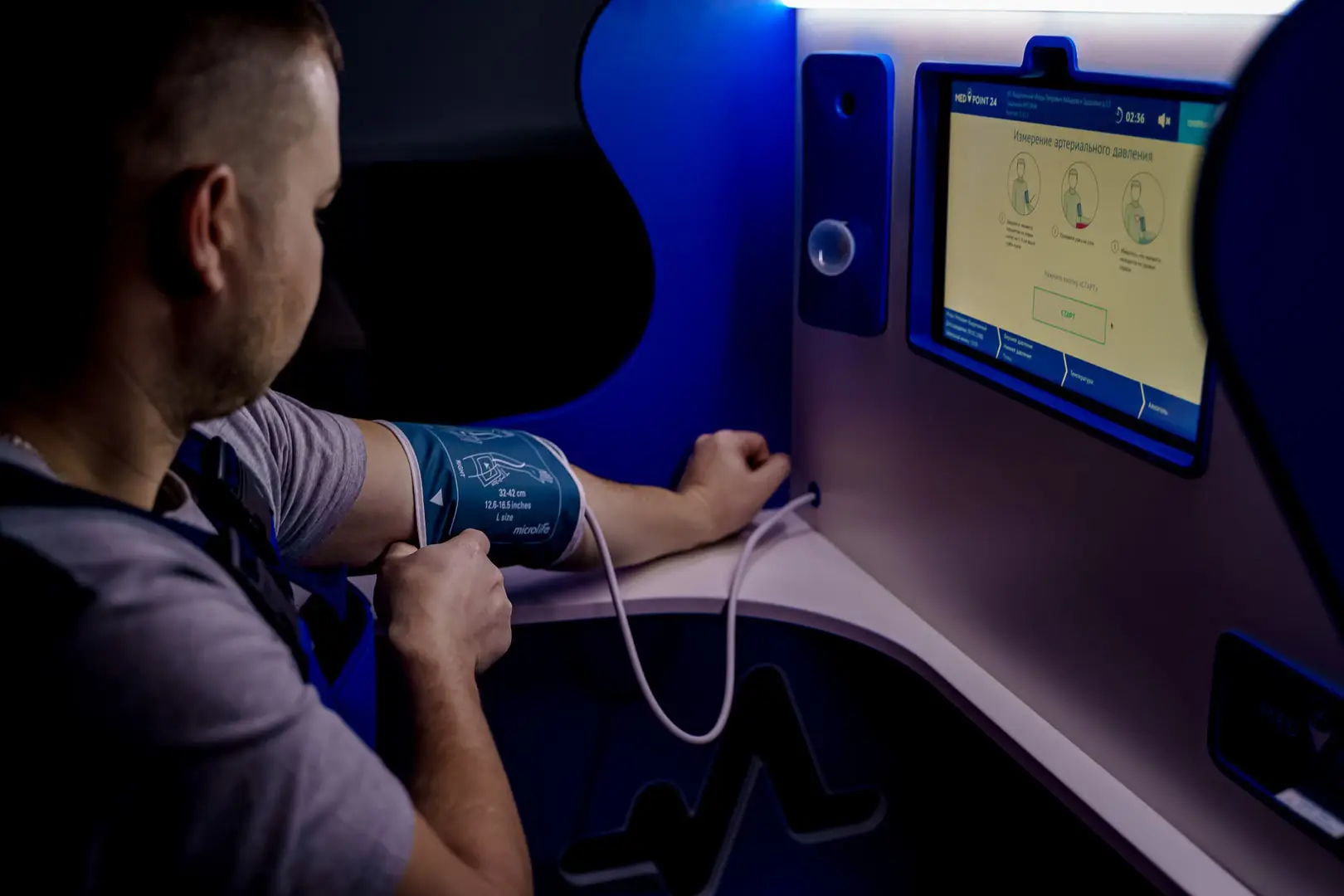
5. Regular Health Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups and screenings are crucial for early detection and management of chronic diseases. Monitor key health indicators such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood glucose levels to catch potential issues before they become serious.





Conclusion
Lifestyle choices are integral to the prevention and management of chronic diseases. By adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, avoiding harmful substances, and managing stress, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing chronic conditions and enhance their overall quality of life. Embracing these healthy habits can lead to a longer, healthier life and improved well-being.